In the fast-evolving world of B2B marketing, thought leadership stands as a cornerstone for...
How to use Lead Scoring with LinkedIn Advertising.
In the fast-paced world of B2B advertising, understanding your target audience and effectively identifying qualified leads is crucial for maximizing campaign success. This article will delve into the concept of lead scoring and explore how it can be leveraged in combination with LinkedIn Advertising to drive meaningful results. We will walk you through the lead scoring strategy, provide examples, and highlight the importance of integrating CRM, personas, for a better understanding of your customer lifecycle.

What is Lead Scoring?
Lead scoring is a method used by B2B advertisers to assign values or scores to leads based on predefined criteria. By assigning scores to leads, marketers can prioritize and focus their efforts on the most promising prospects, improving lead quality and conversion rates. The ultimate goal is to identify leads that are most likely to become customers and nurture them through the sales funnel.
Why is Lead Scoring Important for B2B Advertisers?
Effective lead scoring provides numerous benefits for B2B advertisers. It enables them to:- Identify high-quality leads: By assigning scores to leads, marketers can distinguish between leads that are ready to be engaged and those that require further nurturing.
- Optimize resource allocation: Lead scoring helps allocate marketing resources effectively by prioritizing leads with higher scores, enabling marketers to focus their efforts on prospects with the highest conversion potential.
- Improve conversion rates: By targeting high-scoring leads, marketers can tailor their messaging and offers to meet the specific needs of those prospects, increasing the likelihood of conversion.
- Enhance sales and marketing alignment: By implementing a standardized lead scoring system, marketing and sales teams can align their efforts, facilitating a smoother handoff of leads between departments.
How to develop a Lead Scoring Model?
To implement a successful lead scoring strategy with LinkedIn Advertising, consider the following steps:
1. Defining the Ideal Customer Profile (ICP): Begin by defining your Ideal Customer Profile, which represents the characteristics of your best customers. This includes factors like industry, company size, job titles, and other relevant demographics. Your ICP serves as a benchmark against which leads are evaluated.
2. Creating Buyer Personas: Develop buyer personas that represent the various segments within your target audience. These personas should capture the unique challenges, motivations, and pain points of each segment, allowing you to tailor your messaging and scoring criteria accordingly.
3. Identifying Key Lead Scoring Criteria: Define the key criteria that determine lead quality and conversion potential. These criteria may include factors like job title, company size, engagement with your ads or content, website visits, interactions with your LinkedIn Page, and more.
4. Assigning Point Values to Scoring Criteria: Assign point values to each scoring criterion based on its relative importance in identifying high-quality leads. For example, a lead from a large enterprise might be assigned a higher score than a lead from a small business. Summing up the points for each criterion provides a total lead score, which helps prioritize leads for further action.
Lead Scoring Example with LinkedIn Advertising.
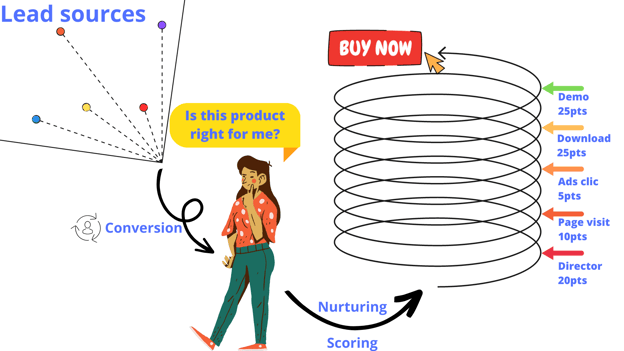
Let's consider an example to illustrate how lead scoring works in the context of LinkedIn Advertising. Suppose you assign the following point values to your scoring criteria:
Job Title: Director (20 points), Manager (10 points), Other (5 points)
Company Size: Enterprise (15 points), Mid-market (10 points), Small Business (5 points)
Engagements with Ads: Clicked on ad (10 points), Liked or shared ad (5 points), No engagement (0 points)
Based on these criteria, a lead with a job title of Director working for an enterprise-level company who clicked on your ad would receive a total score of 45 points, indicating a high-quality lead. On the other hand, a lead with a job title of Manager working for a small business who didn't engage with your ad would receive a total score of 15 points, indicating a lower-priority lead.
Integrating CRM into Lead Scoring.
To further refine your lead scoring, integrate data from your Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system. By analyzing historical customer data and performance, you can identify patterns and behaviors that correlate with successful conversions. This additional information can enhance the accuracy of your lead scoring model.

Leveraging Personas for Effective Lead Scoring.
Buyer personas play a crucial role in lead scoring. By aligning scoring criteria with persona characteristics, you can tailor your lead nurturing strategies and personalize your marketing efforts. For example, if a persona represents the IT decision-maker, their interactions with technical content or engagement with IT-related ads could receive higher scores.
The Role of the Customer Lifecycle in Lead Scoring.
Lead scoring should be adapted to the customer lifecycle stages. Leads in the early awareness stage may receive lower scores compared to leads in the decision or purchasing stage. Aligning lead scoring with the customer lifecycle helps marketers identify where leads are in the buying process and deliver relevant content at each stage, nurturing them towards conversion.
In conclusion, an effective lead scoring is a game-changer for B2B advertisers leveraging LinkedIn Advertising. By implementing a robust lead scoring strategy, you can optimize your marketing efforts, increase conversion rates, and align sales and marketing departments. Integrating CRM data, leveraging buyer personas, and considering the customer lifecycle are vital components for refining your lead scoring model and achieving sustainable success in B2B advertising with LinkedIn. So, take the lead and leverage the power of lead scoring to unlock your B2B advertising potential!

.png?width=50&name=profile-pic%20(8).png)
.jpg?width=250&height=125&name=Project%201%20(1).jpg)